Link Bonding
Overview
Link bonding is a core feature of HyperPath that enables simultaneous data transmission over multiple network interfaces when communicating between nodes. The system creates multiple Peer-to-Peer (P2P) channels between nodes, with each channel utilizing a different network interface pair. Traffic from a single application stream can be intelligently scheduled across these multiple channels, significantly improving throughput and reliability.
Configuration
To configure link bonding on a HyperPath node, you'll need to specify which network interfaces should participate in the bonding process:
- Access the token settings in your HyperPath configuration
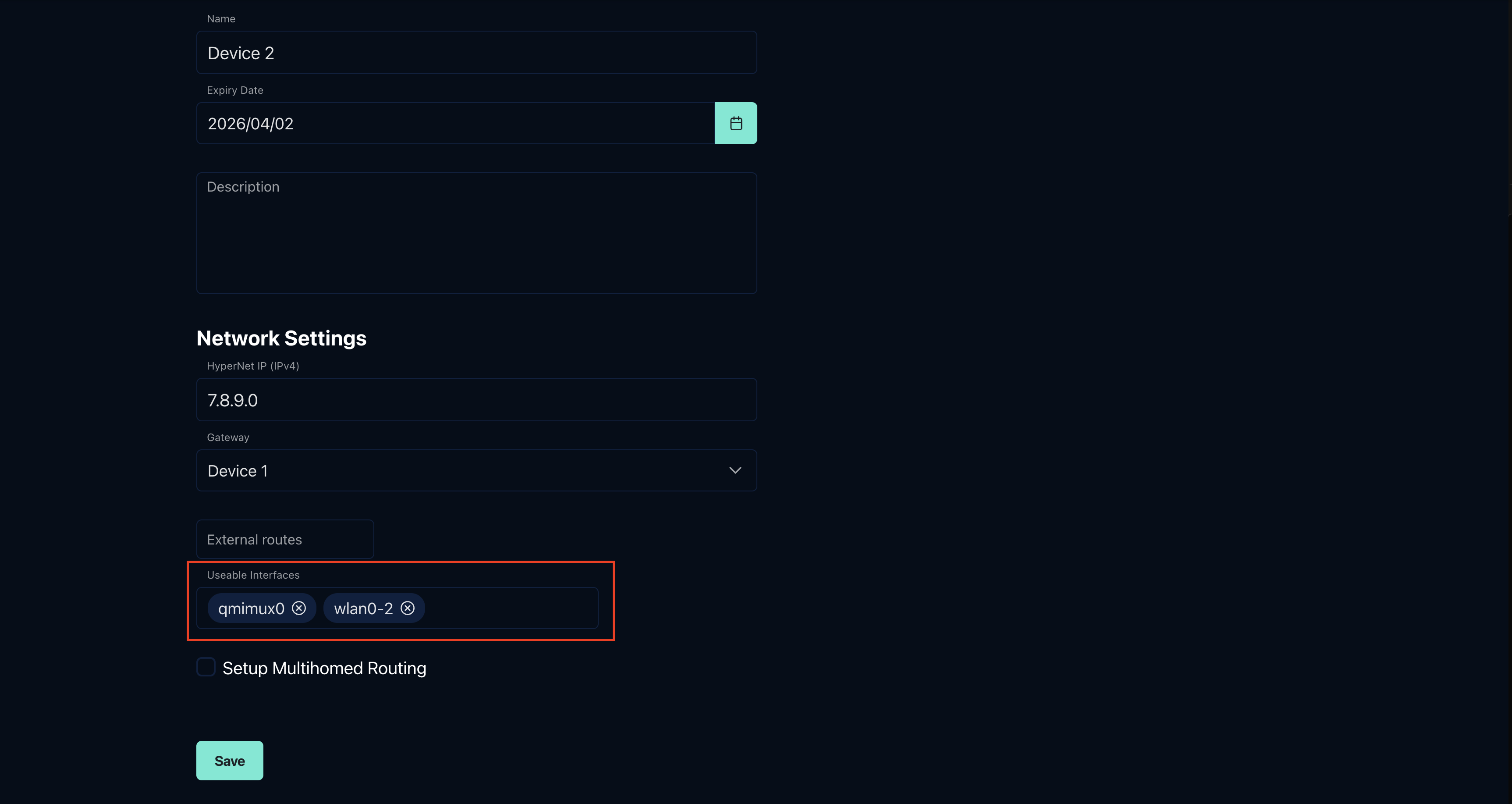
- Locate the
Useable Interfacesparameter - Specify the list of network interfaces that should be used for link bonding
The image below demonstrates how to configure useable interfaces in the token settings:
Scheduling Modes
Currently, HyperPath supports capacity-aggregation as its primary scheduling mode. This mode:
- Utilizes the total capacity of all available interfaces
- Dynamically allocates data across P2P channels based on each channel's time-varying capacity
- Automatically adjusts to changing network conditions for optimal performance
Use Cases
Link bonding can be implemented in several scenarios:
Direct HyperPath Node Communication
A multi-interface HyperPath node can leverage link bonding when connecting to:
- Other HyperPath nodes
- Non-HyperPath devices via intermediary HyperPath nodes
- Internet resources via a HyperPath node acting as a gateway
Gateway Configuration for Non-HyperPath Devices
HyperPath nodes can provide link bonding benefits to standard devices by functioning as a gateway:
- Configure a HyperPath node as a gateway within a WiFi Access Point or router
- Non-HyperPath devices connect to this gateway through a single link (e.g., WiFi)
- The gateway HyperPath node forwards traffic across multiple bonded links to another HyperPath node
- The destination HyperPath node routes traffic to the internet or other network destinations
This configuration effectively turns a HyperPath node into a bonding router that can serve multiple standard devices without requiring special software on those devices.